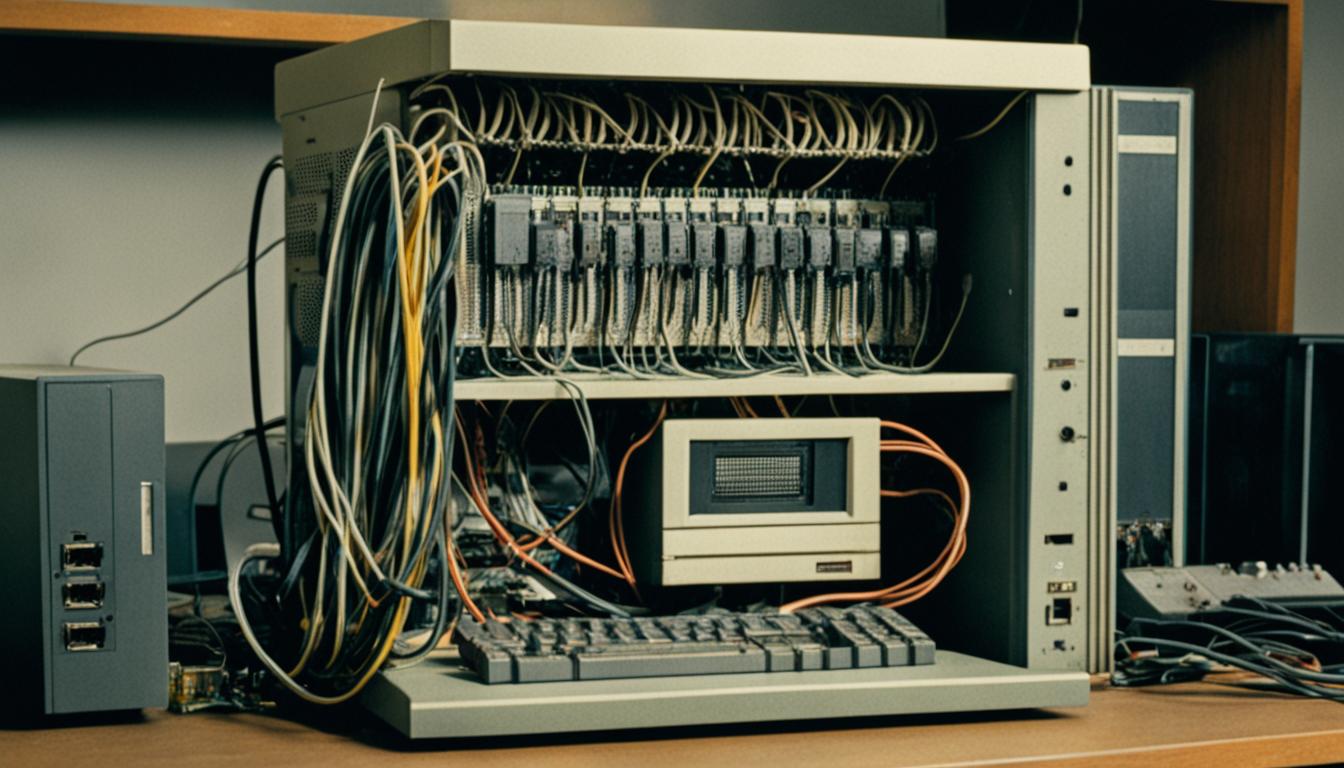
Parallel ports, also known as printer ports or Centronics ports, were once common on early computers. They allowed computers to send multiple bits of data at once. Although they’re not often used in modern computers, they’re still vital for older systems and specific uses.
Many old but still functional systems rely on parallel ports. This includes industrial machines, scientific devices, or old software. Upgrading these to newer interfaces could be expensive and may not work due to compatibility issues.
Some special tasks, like certain data acquisition or control systems, need parallel ports. These jobs were designed with parallel ports in mind and might not support new technology. In some situations, parallel ports offer better performance and reliability than newer alternatives.
Even though new computers don’t usually have parallel ports, there are still ways to use them. USB-to-parallel port adapters let you connect devices needing parallel communication to USB ports. There are also special cards that give computers parallel port abilities.
Even as technology moves forward, we shouldn’t forget the role of parallel ports. They remain crucial for old setups and particular tasks. Their continued importance shows the value of older technology in certain fields.
What is a Parallel Port?
A parallel port is a computer interface used for connecting peripherals like printers. It transfers multiple bits of data at once through parallel wires. This makes data transfer faster than serial ports, which can only send one bit at a time.
These ports were essential for quick communication between computers and devices. They were crucial for printing documents or saving files. Thanks to parallel ports, devices could connect efficiently, improving computer performance.
They enabled quick data exchange between computers and devices. This helped the devices work smoothly and made computers more functional.
Parallel ports could transfer data much faster than serial ports. Because they sent multiple bits at the same time, they were great for high-speed data needs.
But as technology changed, parallel ports became less common. Newer options like USB interfaces replaced them. Still, parallel ports are useful in some older systems and special cases.
In brief, parallel ports connect peripherals and allow for fast data transfer. Their importance has decreased over time. Yet, they were vital in early computing and still matter in certain situations.
The Evolution of Parallel Ports
The Centronics port, or printer port, was key as the main standard for parallel ports. It helped computers talk to printers, scanners, and storage devices. This port became known as IEEE 1284, introducing two new versions: the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and the Extended Capability Port (ECP).
Yet, with tech changes, parallel ports became less common. Now, they’re rare in new computers. USB and network printing, with Ethernet and Wi-Fi, took over.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) changed how we connect gadgets. It’s faster and easier for moving data. We can plug in printers, scanners, and keyboards easily, without the old parallel port hassles.
Network printing lets us print without wires. It’s great for shared spaces. Using Ethernet or Wi-Fi, it lets many users print to one device, boosting work flow.
The Shift Away from Parallel Ports
Tech advances led to using parallel ports less. Devices got smaller, needing less space. This change made parallel ports outdated, replaced by newer tech.
Still, parallel ports have their uses. The gaming world and hobbyists use them. Some even get parallel port effects with gadgets like Raspberry Pi.
Parallel ports show how tech evolves. They remind us that better ways to connect devices always come along. Let’s remember their role as we move forward.
The Advantages and Limitations of Parallel Ports
Parallel ports are great for fast data transfer. They work well with high-speed devices like printers. Most computers used to have them built-in, so you didn’t need extra hardware.
But, parallel ports can’t power devices on their own. Unlike USB ports, they need an external power source for devices like USB-powered drives. Also, they’re not good for two-way communication, making them less versatile.
Connecting many devices to one parallel port can slow things down. If too many devices share the port, you might see slower speeds and data might get lost.
In summary, parallel ports are good for quick data transfer and are usually ready to use on computers. However, their inability to power devices and limited communication options mean they’re not as common anymore.
Conclusion
Parallel ports were once crucial for computer data transfer, but today they’re outdated. The emergence of USB and other interfaces has made them less necessary. Yet, there are still ways to use parallel port functions differently.
The Raspberry Pi lets users mimic parallel port actions with GPIO, I2C, or SPI interfaces. This is great for connecting devices that need parallel ports. In a similar way, Arduino microcontrollers give deep control over hardware, acting as another option for parallel port use.
Technology moves quickly, leaving devices like parallel ports behind. Nowadays, powerful desktop PCs focus on intense computing tasks. Meanwhile, smaller gadgets like smartphones and laptops are becoming more popular. However, in certain areas, such as video gaming, parallel ports on robust computers are still useful.
Even though parallel ports aren’t common now, their impact continues. Devices like the Raspberry Pi and Arduino keep their functions alive through emulation. As technology evolves, staying flexible and exploring new solutions is essential for dealing with changes in computer interfaces.
FAQ
What is a computer with a parallel port used for?
Computers with parallel ports connect to older systems and special apps. They need parallel communication for devices like printers.
What is a parallel port?
A parallel port lets computers send many bits of data at once. It uses several wires arranged side by side.
What types of devices can be connected to a parallel port?
Devices like printers, scanners, and external hard drives connect to a parallel port.
Are parallel ports still commonly used in modern computers?
No, modern computers don’t use parallel ports much. USB and network printing are more common now.
What are the advantages of using a parallel port?
A big plus of parallel ports is fast data transfer. This is great for quick printing.
Are there any limitations to parallel ports?
Yes, parallel ports can’t power devices like USBs. Also, they’re not great for two-way communication.
Can multiple devices be connected to a parallel port?
You can connect many devices, but it might slow down the data speed and not be reliable.
How can parallel port functionality be achieved in modern systems?
A: Raspberry Pi can mimic a parallel port using GPIO, I2C, or SPI. Arduino microcontrollers are also good for controlling hardware.
Why have parallel ports become obsolete?
Newer technology and the rise of better options like USB have made parallel ports outdated.
Where are parallel ports still required?
Some fields, like the video game industry, still need powerful computers with parallel ports.