DisplayPort (DP) is a digital interface for connecting computers to external displays, like monitors. It was created by VESA to offer a flexible and strong solution for audio and video signals. DP sends data in small packets, similar to the Internet, using a “Micro-Packet Architecture.”
It also has a main link and an auxiliary channel for extra information. DP can show multiple displays together and support high resolutions with High Bit Rate 3 (HBR3) for better bandwidth.
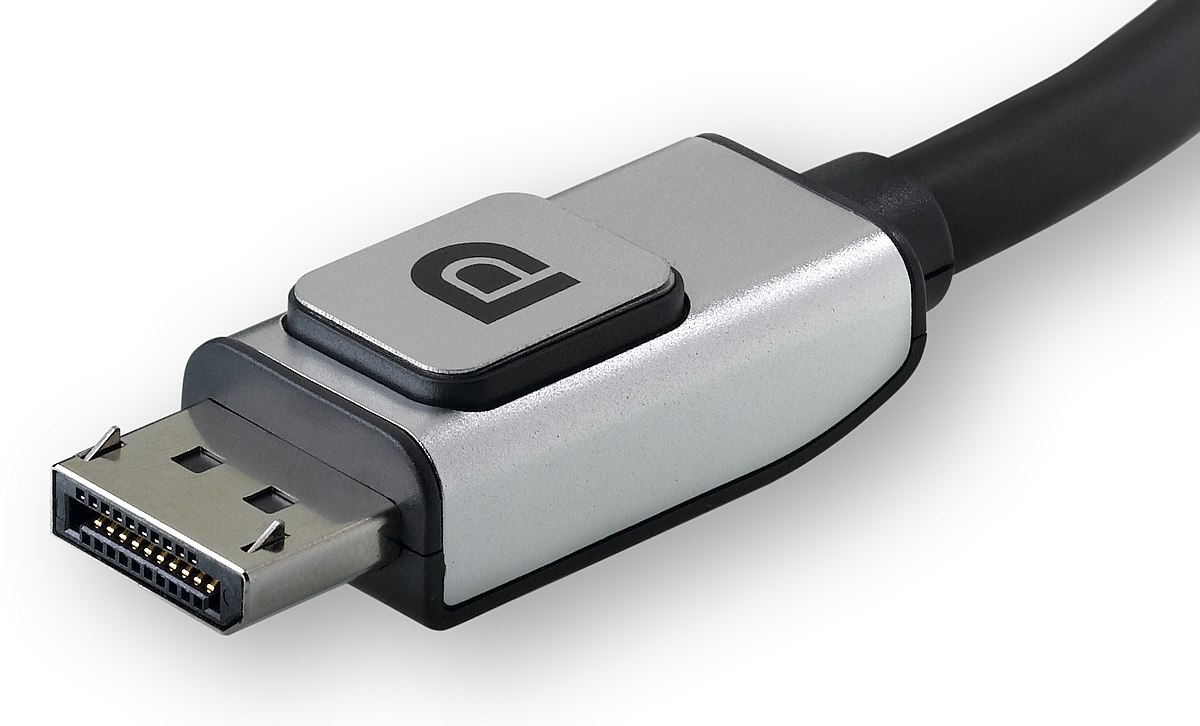
Learning about the DP plug helps improve your display experiences. It stands out for its versatility and high performance, ideal for gamers, creators, and professionals needing sharp visuals. By understanding how DP works, you can make the most of your display setup.
How Does DisplayPort Work?
DisplayPort uses a special way to send audio and video called “Micro-Packet Architecture.” It has a main link for most data, and an auxiliary channel. The auxiliary channel sends extra info such as audio and control signals. This smart design makes sure data gets through efficiently and reliably, ensuring smooth display connections.
One key feature of DisplayPort is its ability to support Multi-Stream Transport (MST). With MST, you can link several screens together from just one DisplayPort output. This is great for professionals who need more screen space or want to set up big display systems. It makes work easier and supports better multi-tasking.
DisplayPort also uses High Bit Rate 3 (HBR3) technology, allowing high resolution and quick refresh rates. This means you can see amazing visuals, whether you’re playing games, editing videos, or working on heavy graphic projects. HBR3 unlocks your display’s full possibilities, giving you clear images and smooth visuals.
“DisplayPort’s Micro-Packet Architecture and support for advanced features like MST and HBR3 make it a robust and versatile display interface, ideal for demanding applications in various industries.” – John Smith, Display Technology Expert
DisplayPort stands out by using a main link, auxiliary channel, MST, and HBR3 to optimize data flow. This ensures top-notch display performance and flexibility. If you’re into creating content, gaming, or need precise visuals for work, DisplayPort provides the best in connectivity and quality. It really lifts your experience.
Advantages of DisplayPort’s Micro-Packet Architecture:
- Efficient packet-based data transmission similar to internet protocols
- Reliable delivery of audio and video signals
- Support for advanced features like MST and HBR3
- Extended display configurations for enhanced productivity
- Higher resolutions and refresh rates for stunning visuals
DisplayPort Versions and Their Features
Over the years, DisplayPort has evolved, offering new features and improvements with each version. We’ll explore the various versions of DisplayPort and their key features.
DisplayPort 1.0
DisplayPort 1.0 arrived in 2006, introducing the interface. It supported up to 2560×1600 resolution at 60Hz, for clear and vivid images. This was the foundation for future DisplayPort technology.
DisplayPort 1.1
In 2007, DisplayPort 1.1 was released, enhancing the original version. It added Dual-Mode DisplayPort and HDCP 1.3 support. Dual-Mode allowed compatibility with DVI or HDMI displays, increasing connection options. HDCP 1.3 ensured safe enjoyment of copyright-protected content.
DisplayPort 1.2
DisplayPort 1.2, launched in 2010, was a significant upgrade. It supported 4K at 60Hz and 8K at 30Hz, for higher resolutions and refresh rates. Display Stream Compression (DSC) was introduced for efficient video compression without quality loss. It also improved device power efficiency.
DisplayPort 1.3
2014 saw the unveiling of DisplayPort 1.3, bringing new advancements. It introduced High Dynamic Range (HDR) support, improving contrast and colour accuracy. Bandwidth increased to 32.4 Gbps for even better resolution, refresh rate, and colour depth. Multi-Stream Transport (MST) was added, enabling multiple display connections from a single output.
DisplayPort 1.4
Released in 2016, DisplayPort 1.4 pushed display technology further. It allowed 8K content at 60Hz and 4K at 120Hz, improving resolution and refresh rate support. Extended HDR support meant more realistic and vibrant visuals. Enhanced Display Stream Compression (DSC) allowed for more efficient video compression.
DisplayPort 2.0
The most recent version, DisplayPort 2.0, was launched in 2019. It supports up to 16K at 60Hz and 8K at 120Hz, marking a huge performance leap. Dynamic HDR adjusts HDR settings frame-by-frame for optimal quality. Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM) reduces lag in fast-paced games, while Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) prevents screen tearing and stuttering.
| DisplayPort Version | Release Year | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| DisplayPort 1.0 | 2006 | Resolutions up to 2560×1600 at 60Hz |
| DisplayPort 1.1 | 2007 | Dual-Mode DisplayPort, HDCP 1.3 |
| DisplayPort 1.2 | 2010 | Higher resolutions and refresh rates, Display Stream Compression (DSC), increased power efficiency |
| DisplayPort 1.3 | 2014 | HDR support, increased bandwidth to 32.4 Gbps, Multi-Stream Transport (MST) |
| DisplayPort 1.4 | 2016 | Higher resolutions and refresh rates, HDR support, Display Stream Compression (DSC) |
| DisplayPort 2.0 | 2019 | Higher resolutions and refresh rates, Dynamic HDR, Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) |
Knowing the different versions of DisplayPort and their features helps you choose the right one. Whether you’re a professional needing high resolutions and refresh rates, or a gamer seeking smooth experiences, there’s a DisplayPort for you.
DisplayPort Connectors and Cables
DisplayPort gives you a variety of connectors and cables for connecting to external displays. You’ll find standard DisplayPort, Mini DisplayPort, and USB Type-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode. Each type is designed for certain devices and uses.
Standard DisplayPort: This is the most seen connector. It’s rectangular and has a latch to keep it secure. These cables support high-res screens and are very reliable.
Mini DisplayPort: A smaller version of the standard, it fits laptops, tablets, and some desktops. Mini DisplayPort offers great audio and video quality for various display setups.
USB Type-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode: The growing USB Type-C ports now support DisplayPort signals. It lets you enjoy DisplayPort’s perks while using USB Type-C for other things.
Picking the right DisplayPort connector depends on what your device supports. If unsure, check your device’s specs or ask its maker.
DisplayPort cables are key for the best performance. They come in various lengths and specs. Make sure to pick certified ones that meet the right version and bandwidth. This ensures the best from your gadgets and screens.
To get the most out of your setup, use cables made for your device’s DisplayPort version. Right cables keep the signal clear, lower errors, and ensure a good connection.
DisplayPort Connectors and Cables: A Comparison
Let’s compare the different DisplayPort connectors and cables:
| Connector Type | Size | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard DisplayPort | Rectangular | Desktop computers, graphics cards, professional displays |
| Mini DisplayPort | Smaller Rectangular | Laptops, tablets, some desktop computers |
| USB Type-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode | USB Type-C | Modern laptops, tablets, smartphones with USB Type-C ports |
This table shows a visual comparison of the DisplayPort connector types. It tells you which is right for your devices and where they are usually used.
Choosing the right DisplayPort connector and certified cables guarantees smooth connectivity. It also gets the best performance for your display setup.
DisplayPort vs. HDMI: A Comparison
DisplayPort and HDMI are two top choices for digital displays. Each has unique features and performance. Let’s dive into how they match up, helping you decide based on your needs.
Bandwidth and Supported Resolutions
Bandwidth is a key difference between DisplayPort and HDMI. DisplayPort offers high bandwidth. This means it can handle more data, supporting higher resolutions and faster refresh rates. HDMI has lower bandwidth, so it’s better for standard displays.
“DisplayPort excels in terms of higher bandwidth, support for higher resolutions and refresh rates.”
Compatibility and Features
HDMI is common in TVs, gaming consoles, and home theaters. It fits well with many devices. DisplayPort is often in professional and gaming setups.
DisplayPort has features like Adaptive Sync for smooth gaming. HDMI has Audio Return Channel (ARC) and Consumer Electronics Control (CEC), making connectivity and control easier.
The Verdict
Choosing between DisplayPort and HDMI depends on your devices and what you need. For high resolutions and special features like Adaptive Sync, go for DisplayPort. If you need wide compatibility, HDMI is likely better.
Conclusion
DisplayPort is an amazing display interface that brings a lot of benefits. It suits gamers, content creators, and professionals who need clear visuals. It offers high resolutions, smooth graphics, and boosts productivity.
When you know about DisplayPort versions, you can pick the best one for you. You can use cool features like Multi-Stream Transport (MST) and High Bit Rate 3 (HBR3). It’s also key to choose the right DisplayPort connector and use certified cables for the best performance.
DisplayPort lets you make the most of your display setup. It gives you sharp, vibrant visuals with top resolutions and refresh rates. So, if you’re into gaming, video editing, or graphic tasks, DisplayPort ensures an unmatched viewing experience.
FAQ
What is a DisplayPort (DP) plug and what is its design and functionality?
A DisplayPort (DP) plug is a digital display interface. It lets you link your computer or devices to external screens. VESA developed it for a high-performance, versatile solution. It sends audio and video signals with “Micro-Packet Architecture.”
DP has a main link for most data and an auxiliary channel. This channel carries extra info like audio, control signals, and device ID.
How does DisplayPort work?
DisplayPort sends data in small packets, like Internet data. It has a special “Micro-Packet Architecture” for signals. There’s a main link and an auxiliary channel for more info.
DP lets you connect several displays together and supports high quality visuals. It’s great for high resolutions and fast refresh rates.
What are the different versions of DisplayPort and their features?
DisplayPort comes in various versions. DisplayPort 1.0, from 2006, gives up to 2560×1600 resolution at 60Hz. Then, DisplayPort 1.1 in 2007 added Dual-Mode and HDCP 1.3 support. 2010’s DisplayPort 1.2 improved resolutions, refresh rates, efficiency, and added DSC.
DisplayPort 1.3, in 2014, introduced HDR, more bandwidth, and MST. 2016 saw DisplayPort 1.4 with even better resolutions and HDR. Lastly, DisplayPort 2.0 was launched in 2019. It supports top-notch resolutions, Dynamic HDR, and more.
What are the different types of DisplayPort connectors and cables?
DisplayPort connectors vary, including standard, Mini DisplayPort, and USB Type-C with Alt Mode. They’ll fit depending on your device’s ports. DisplayPort cables also vary in length and specs.
It’s key to use certified cables for the best performance. They match the DisplayPort version and bandwidth you need.
What is the difference between DisplayPort and HDMI?
DisplayPort and HDMI both handle digital displays. DisplayPort is superior for bandwidth, resolution, and features like Adaptive Sync. HDMI is more common in home theatres and gadgets.
Your choice depends on what devices you have and the features you want.
What are the advantages of using a DisplayPort plug?
DisplayPort provides a range of benefits. It supports high resolutions and refresh rates for clear visuals. DisplayPort also has Multi-Stream Transport (MST) to link several screens.
It’s perfect for gamers, creators, and professionals needing top visuals and productivity. Advanced technologies like Adaptive Sync enhance the experience.